Argentina is a high-income country in South America. Its population was 46.6 million people in 2023, and life expectancy was 76 years in 2022. The public sector, social security and the private sector together make up Argentina’s health system. The public sector provides free medical care financed by general and earmarked taxes. The Ministry of Health and provincial jurisdictions are responsible for redistributing these funds. The social security funds and the National Institute of Social Services for Retirees and Pensioners (PAMI) constitute the national social health security. Compulsory contributions from employees and employers finance these social security funds. The National Health Insurance System was created to provide equal and integral health benefits. Direct payments by patients and voluntary health insurance subscribers finance private sector insurers and service providers.
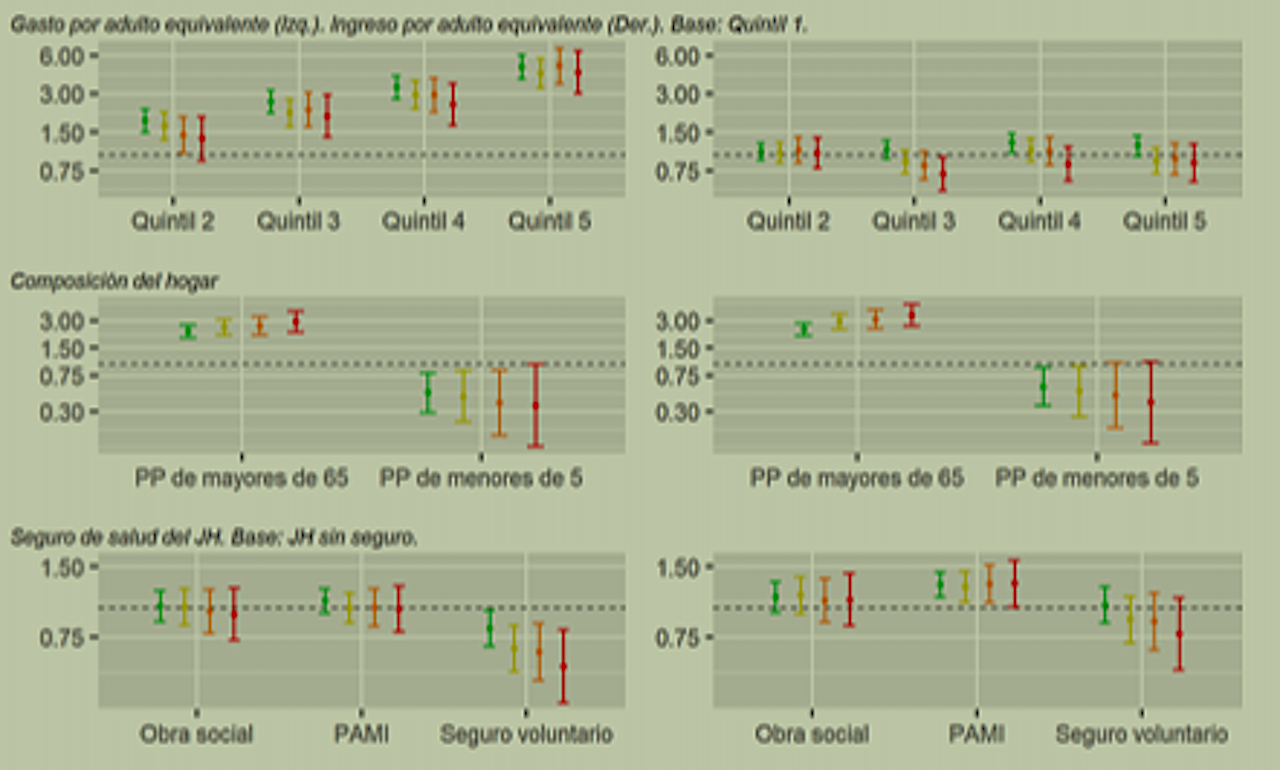
High out-of-pocket expenditure despite public financing
Remaining challenges
References
[1] World Health Organization, Global Health Expenditure Database, Indicators and Data (choose country)
[2] World Health Organization, Health Financing and Economics, WHO Health Financing Dashboard (choose country)