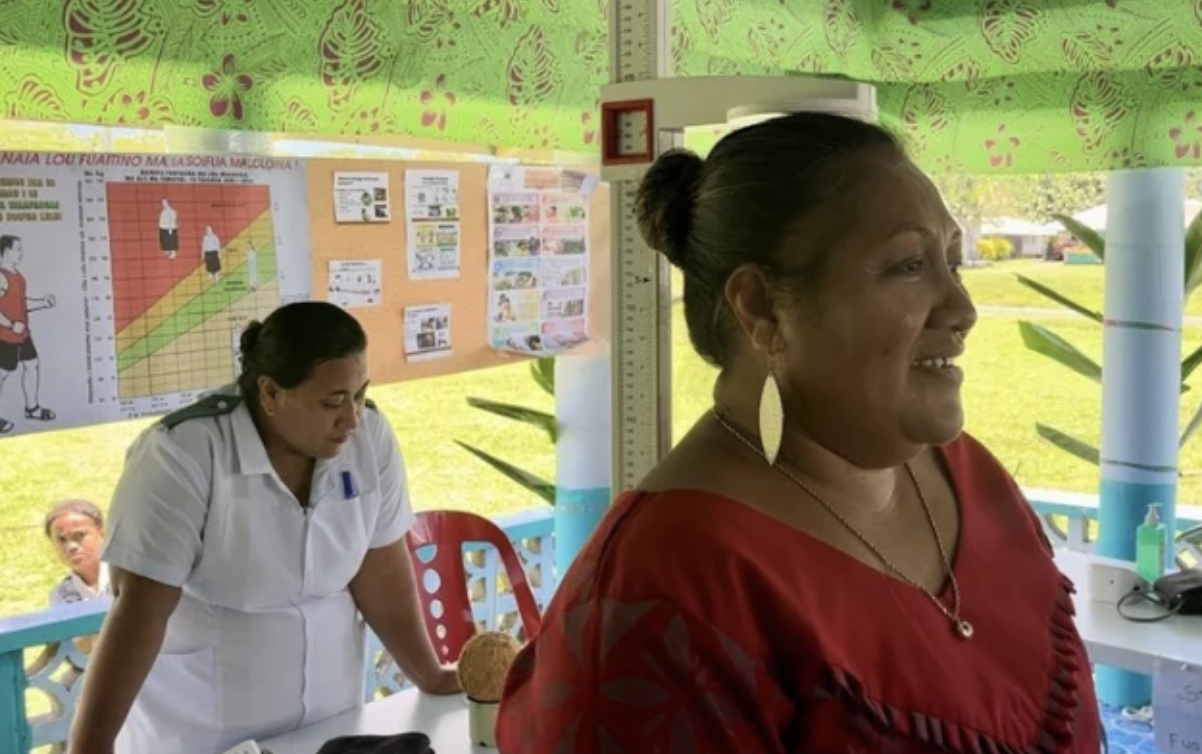
Tuvalu’s gross national income per capita in 2020 was US$ 5,820. Categorized as a fragile state, Tuvalu is one of the world’s smallest, most remote, and most climate-change–vulnerable countries. Its nine inhabited islands total 26 square kilometers over one-half million square kilometers of the western Pacific Ocean. Tuvalu is one of the most densely populated countries in the world, with a population of 11.2 thousand people in 2021. Tuvalu – Health Systems Strengthening Project reports all the data and information about Tuvalu summarized here, unless otherwise noted.
High disease burden caused by noncommunicable diseases
High commitment of government to funding health needs
Total health expenditure as a share of GDP is 24% with per capita health expenditure of US$ 973 in constant 2019 US dollars. All health services in Tuvalu are free, and the majority of the health system is funded, delivered or arranged by the government. This arrangement ensures a high level of financial protection. Tuvaluans are not vulnerable to impoverishment in accessing health care. Current health expenditure (CHE) is sourced largely from general domestic revenue (84% in 2021). However, there is a high reliance on external financing, which in 2021 was 14% of CHE). Out-of-pocket expenditure is consistently less than 1% of CHE.
Because health services depend heavily on government funding, a tightening fiscal space and declining tax revenues (due to the COVID-19 pandemic) have put the delivery of health services at risk.