The study aims to assess whether the presence of older adults and of a head of household who is a beneficiary of the Comprehensive Health Care Program in households in Argentina are associated with a higher probability of incurring catastrophic health care expenses.
Using data from the National Household Expenditure Survey of the National Institute of Statistics and Census, estimates are made of the determinants of catastrophic health expenditure in Argentina.
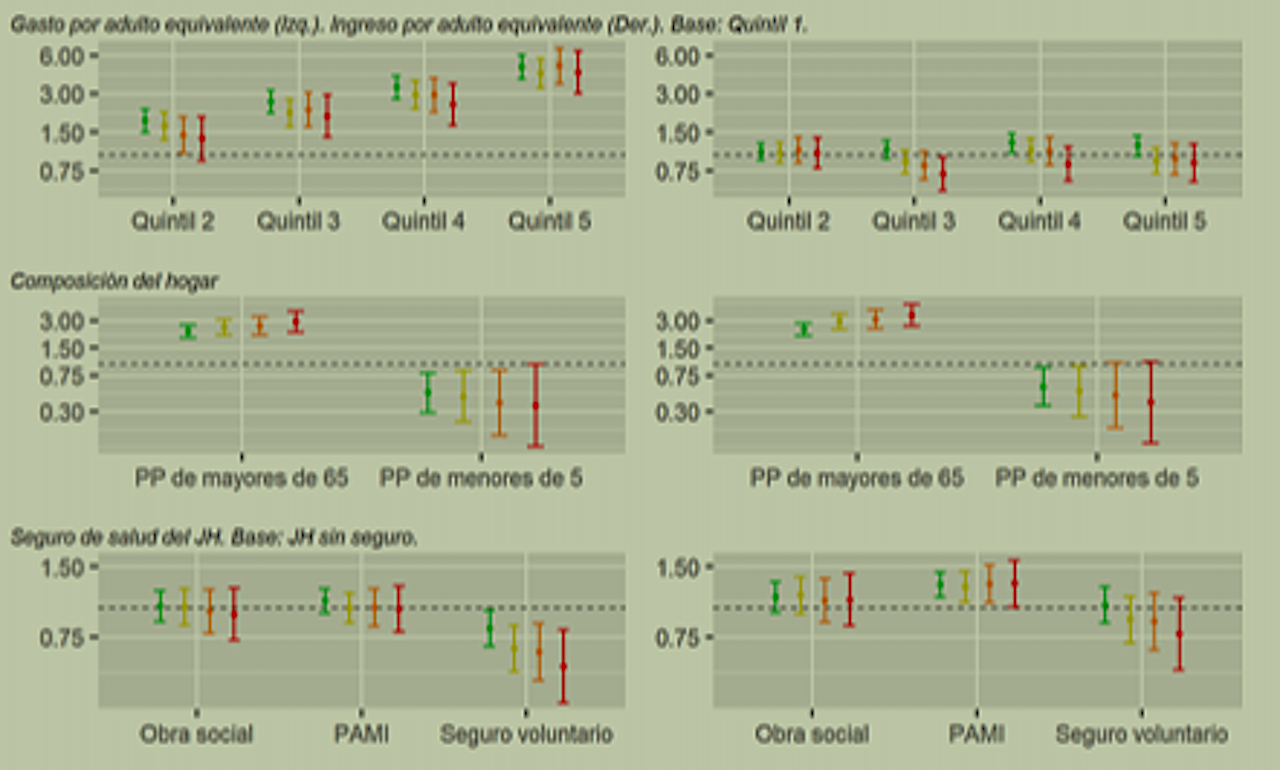
The results show that households with greater consumption capacity are more likely to incur catastrophic health spending. The presence of older adults in the household increases the estimated probability of incurring catastrophic health spending. When analyzing the effect of health insurance, it is observed that only the fact that the head of household has voluntary insurance is associated with a lower probability of incurring catastrophic health expenses.