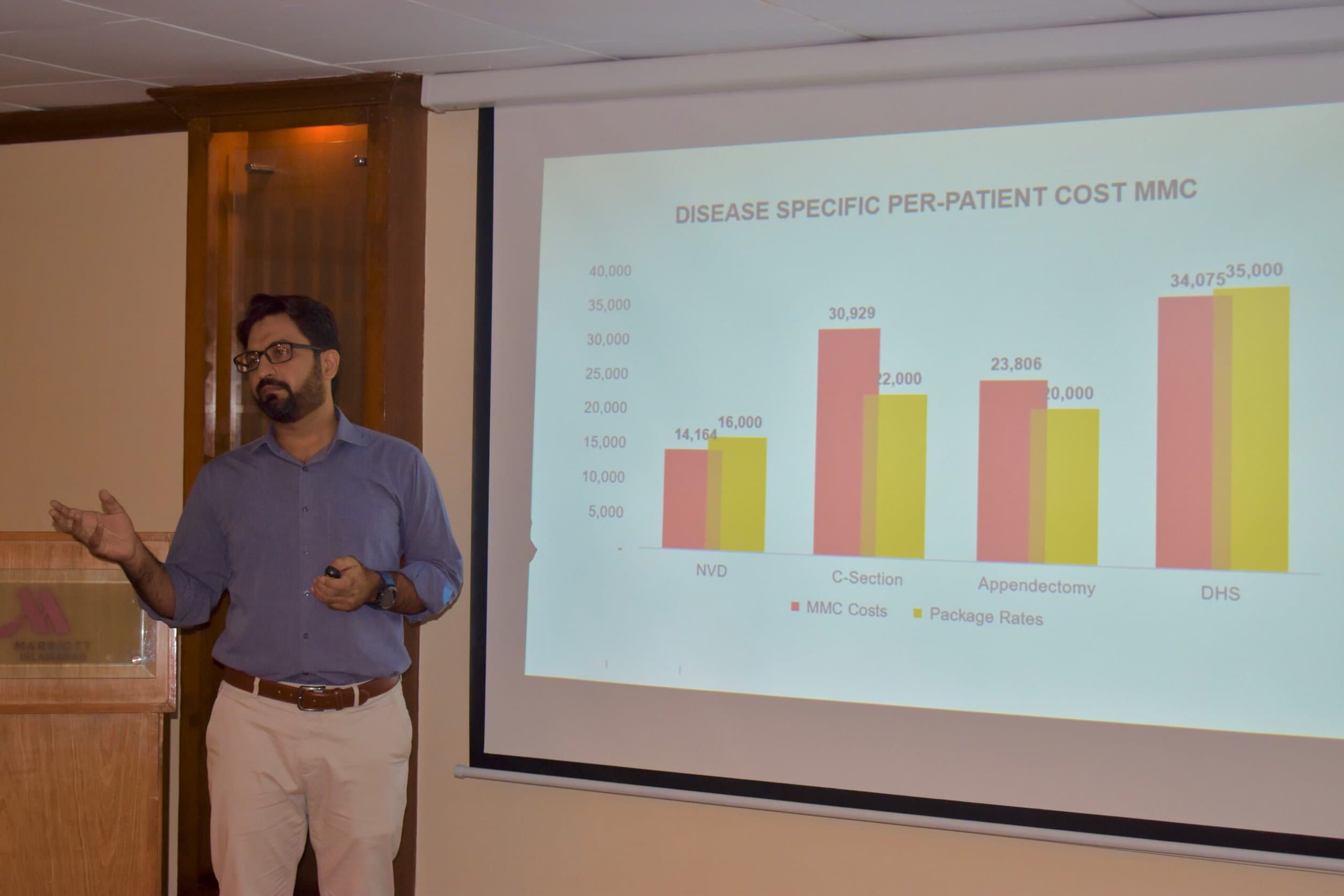
P4H Network has contributed to the costing study in Africa that GIZ has supported, among others, through its country focal person and health adviser in Tanzania.
The Healthy DEvelopments article explores a series of complex costing studies supported by GIZ across Africa and Asia, focusing on the lessons learned from these projects. Over two decades, GIZ has backed various studies to better understand the costs of healthcare services in low- and middle-income countries, aiming to inform national health and financing plans. Despite the rationales for these studies, the lack of skills and inadequate information at health facilities have presented significant challenges. The article discusses these obstacles and the need for political and technical expertise to navigate the complexities of health sector financing.
Kai Straehler-Pohl, who was a Health Advisor for P4H, was involved in the Tanzania costing study. He emphasized that for costing studies to be effective, those involved must have the power and autonomy to implement changes based on the study results. This underscores the need for strong stakeholder engagement and political support for health sector reforms. Similarly, Kuki Tarimo, the current P4H Focal Point for Tanzania, reflects on the importance of involving national academic and specialist institutions in costing studies instead of relying solely on external consultants. This approach promotes local capacity building and ensures that studies are more rooted in the country’s context.
The broader context of the article underscores the importance of effective costing studies in guiding health sector reforms and ensuring equitable access to healthcare. The challenges faced by GIZ-supported studies suggest that strategic planning, collaboration, and a deep understanding of political dynamics are crucial to the success of such projects. The involvement of P4H and its focus on capacity building and stakeholder collaboration suggest that a networked approach can help address these challenges and lead to more sustainable health financing solutions.