Hot off the press – Groundbreaking report on Global Health Financing from WHO
Shaping the future of Health Systems : lessons from Global health expenditure
Things are moving fast in the health sector! Global expenditure in health illustrate this trend, which the latest report on global health financing from the World Health Organization underlines and analyses in depth. The WHO report, prepared under the leadership of WHO Director for Health Systems Governance and Financing Dr Agnès Soucat and Joe Kutzin, Co-ordinator of Health Financing at the UN Health Agency, was officially launched on 20 February 2019.
It confirms dynamics that shape the future of health systems on the road to Universal Health Coverage. In particular, it underscores the swift growth of health expenditure, which is increasing at a faster pace than the rest of economy. This is particularly true in low and middle income countries where health spending is growing at over 6% annually compared with 4% in high income countries on average.
In low and middle income countries where health spending is growing at over 6% annually compared with 4% in high income countries on average.
The figures above outline an emerging norm: government health expenditure is central and is increasing with economic growth as well as general government spending. In middle income countries, government health expenditure per capita has doubled since the year 2000. On average, governments now spend on health US$60 per person in lower-middle income countries and close to US$250 in upper-middle income countries.
This is indeed a positive development which the World Health Organization commends. However, thre is still room for improvement to make health care more equitable and accessible for all, and ultimately progress towards Universal Health Coverage.
Health expenditure…..bolstering the 3 billion target ?
Insights from WHO published in the report highlight that health systems which rely more on public spending offer people better financial protection. More government spending is often associated with better coverage of essential services but it doesn’t always reduce inequities in access: the efficiency and allocation of public spending matter! This is potentially key to meet the 3 billion-target heralded by WHO, an ambition that has garnered immense support from world leaders.
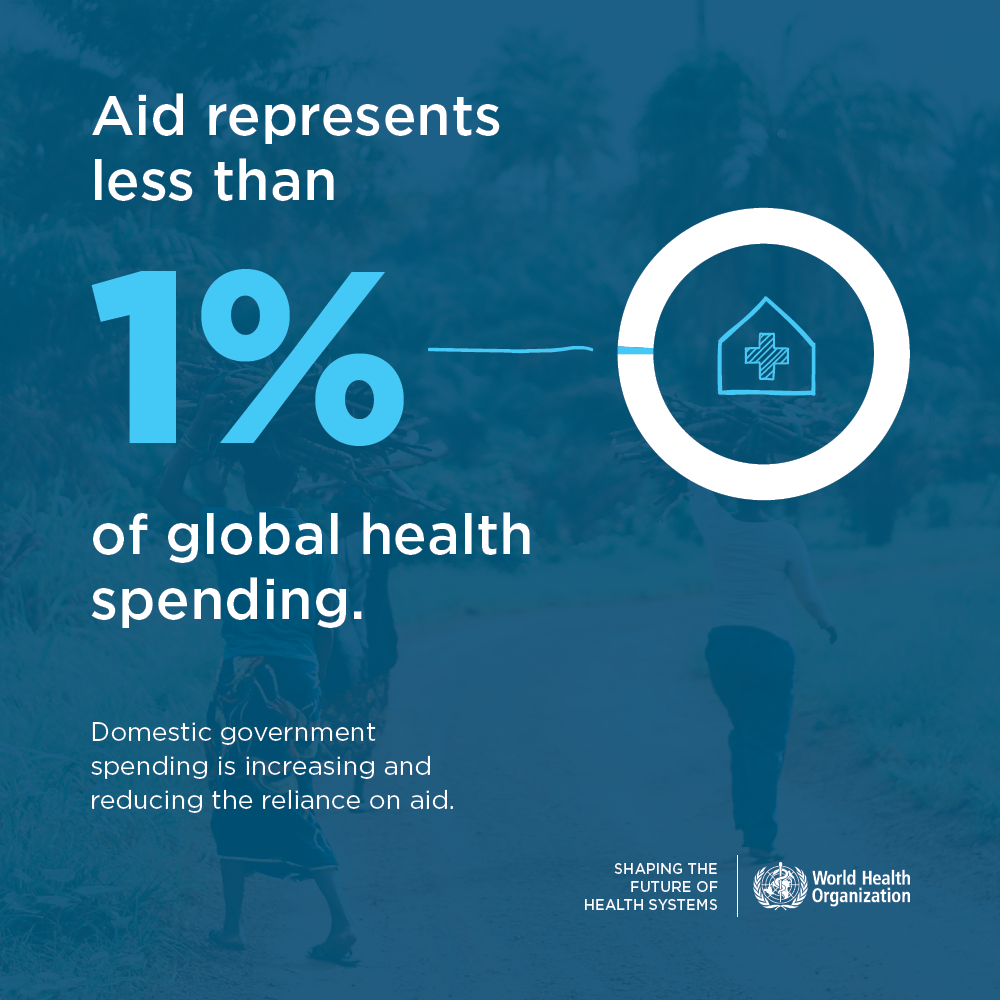
On the road to Universal Health Coverage and Health for All, the picture is not yet quite complete. WHO’s report offers unprecedented insight in the role of external aid in health. While the report clearly underlines that middle income countries are transitioning to domestically fund health systems, aid is still essential to many countries, particularly low-income countries.
A key finding of the report is that external aid represents 1% of global health expenditure only.
A breakdown of this figure shows how aid is spent in low and middle income countries. Currently almost 50% of external funds are devoted to three diseases – HIV/AIDS, TB and malaria – another 10% is spent on reproductive health and a further 10% on non-communicable diseases.
The latest data shows that most low-income countries still rely on external funding for immunization and for responding to pandemics.
PHC : the only game in town ?
The WHO report attempts for the first time to bring together expenditure data on Primary Health Care. As the Alma-Ata Declaration celebrates its 40 years of existence, it is essential to revisit the foundations of effective health systems : primary health care is the key to getting closer to universal health coverage.
In low and middle income countries, new data suggests that more than half of health spending is devoted to primary health care. Governments fund less than 40% of this spending though. In sum, governments are investing more and there is a transformation underway, which is clearly visible through the expenditure trends.
Finger on the pulse ? From expenditure trends to policy advice
Efforts are still required though if we are going to make progress along the path to UHC and achieve the Sustainable Development Goals. The new WHO report on global health expenditure describes advances made around the world and points to ways that policy makers, health professionals and citizens alike can continue to strengthen health systems.
Health is a priority for all and an investment in our future. Health is a human right : to entrench this political commitment in the reality of equitable access for all people to the care they need, financing efforts as well as attention to efficiencies and cost-effectiveness have to be sustained. This is how the 3 billion target can be reached.
The drive beyond the strong analytics provided by WHO in this report is the same that underpins every research, action or operation across the organization:
“Health is a human right. No one should get sick or die just because they are poor, or because they cannot access the services they need.” − Dr Tedros
Download the report: click here
If you want to know more: watch the video !
{“preview_thumbnail”:”/sites/default/files/styles/video_embed_wysiwyg_preview/public/video_thumbnails/EIMh2i_lBWQ.jpg?itok=Vijx7nua”,”video_url”:”https://youtu.be/EIMh2i_lBWQ”,”settings”:{“responsive”:1,”width”:”854″,”height”:”480″,”autoplay”:0},”settings_summary”:[“Embedded Video (Responsive).”]}
In a nutshell…Key messages from the report
- Fast growth – Health is booming!
Health spending is 10% of global GDP and is growing faster than GDP!
- PHC…Mind the gap
More than 50% of health spending in low and middle income countries goes to PHC
However, less than 40% of all PHC spending comes from governments
- Aid and the transition
Domestic funding is essential and is the key to UHC
Aid is still important for many countries. It represents now less than 1% of global health expenditure.
- Health…a net contributor to social and economic development
Health is a priority for all and an investment in our future